(arstechnica.com)
WASHINGTON, DC—This week, NASA’s new administrator, Jared Isaacman, said he has “full confidence” in the space agency’s plans to use the existing heat shield to protect the Orion spacecraft during its upcoming lunar mission.
Isaacman made the determination after briefings with senior leaders at the agency and a half-day review of NASA’s findings with outside experts.
“We have full confidence in the Orion spacecraft and its heat shield, grounded in rigorous analysis and the work of exceptional engineers who followed the data throughout the process,” Isaacman said Thursday.
Isaacman has previously indicated that reviewing the heat shield issue early in his tenure, especially with the Artemis II mission due to launch in as few as four weeks, was a top priority. He met with senior agency officials about the matter within hours of being sworn in on December 18.
The private astronaut and billionaire entrepreneur has also said there should be more public transparency at NASA.
Following the Artemis I mission in November 2022, NASA was roundly criticized for its opaque handling of damage to Orion’s heat shield. The seriousness of the problem was not disclosed for nearly a year and a half after the Artemis I mission, when NASA’s Inspector General finally published close-up images of char loss—chunks of ablative material at Orion’s base that were intended to protect the spacecraft during its return but had fallen away.
To address these concerns, NASA tapped an “independent review team” in April 2024 to assess the agency’s investigation of the heat shield. This group’s findings were finalized in December 2024, at which time NASA formally decided to fly the Artemis II mission with the existing heat shield. Although NASA held a news conference to discuss its conclusions, a publicly released copy of the independent review team’s report was heavily redacted, creating further doubt about the integrity of the process. Some notable critics assailed NASA’s decision to fly on the heat shield as is and decried the ongoing lack of transparency.
That is more or less where the matter stood until a few days before Christmas, when Isaacman officially became NASA administrator.
Transparency for the taxpayer
After taking the job in Washington, DC, Isaacman asked the engineers who investigated the heat shield issue for NASA, as well as the chair of the independent review team and senior human spaceflight officials, to meet with a handful of outside experts. These included former NASA astronauts Charles Camarda and Danny Olivas, both of whom have expertise in heat shields and had expressed concerns about the agency’s decision-making.
For the sake of transparency, Isaacman also invited two reporters to sit in on the meeting, me and Micah Maidenberg of The Wall Street Journal. We were allowed to report on the discussions without directly quoting participants for the sake of a full and open discussion.
The inspector general’s report, released on May 1, 2024, included new images of Orion’s heat shield.
Credit: NASA Inspector General
The inspector general’s report, released on May 1, 2024, included new images of Orion’s heat shield. Credit: NASA Inspector General
Convened in a ninth-floor conference room at NASA Headquarters known as the Program Review Center, the meeting lasted for more than three hours. Isaacman attended much of it, though he stepped out from time to time to handle an ongoing crisis involving an unwell astronaut on orbit. He was flanked by the agency’s associate administrator, Amit Kshatriya; the agency’s chief of staff, Jackie Jester; and Lori Glaze, the acting associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate. The heat shield experts joined virtually from Houston, along with Orion Program Manager Howard Hu.
Isaacman made it clear at the outset that, after reviewing the data and discussing the matter with NASA engineers, he accepted the agency’s decision to fly Artemis II as planned. The team had his full confidence, and he hoped that by making the same experts available to Camarda and Olivas, it would ease some of their concerns.
What followed was a spirited discussion, with Camarda sparring regularly with the presenters and Olivas asking questions more infrequently. The engineering team in Houston, led by Luis Saucedo, went through dozens of charts and presented reams of data that had not been made public before.
“That level of openness and transparency is exactly what should be expected of NASA,” Isaacman said after the meeting.
“What if we’re wrong?”
Perhaps the most striking revelation was what the NASA engineers called “what if we’re wrong” testing.
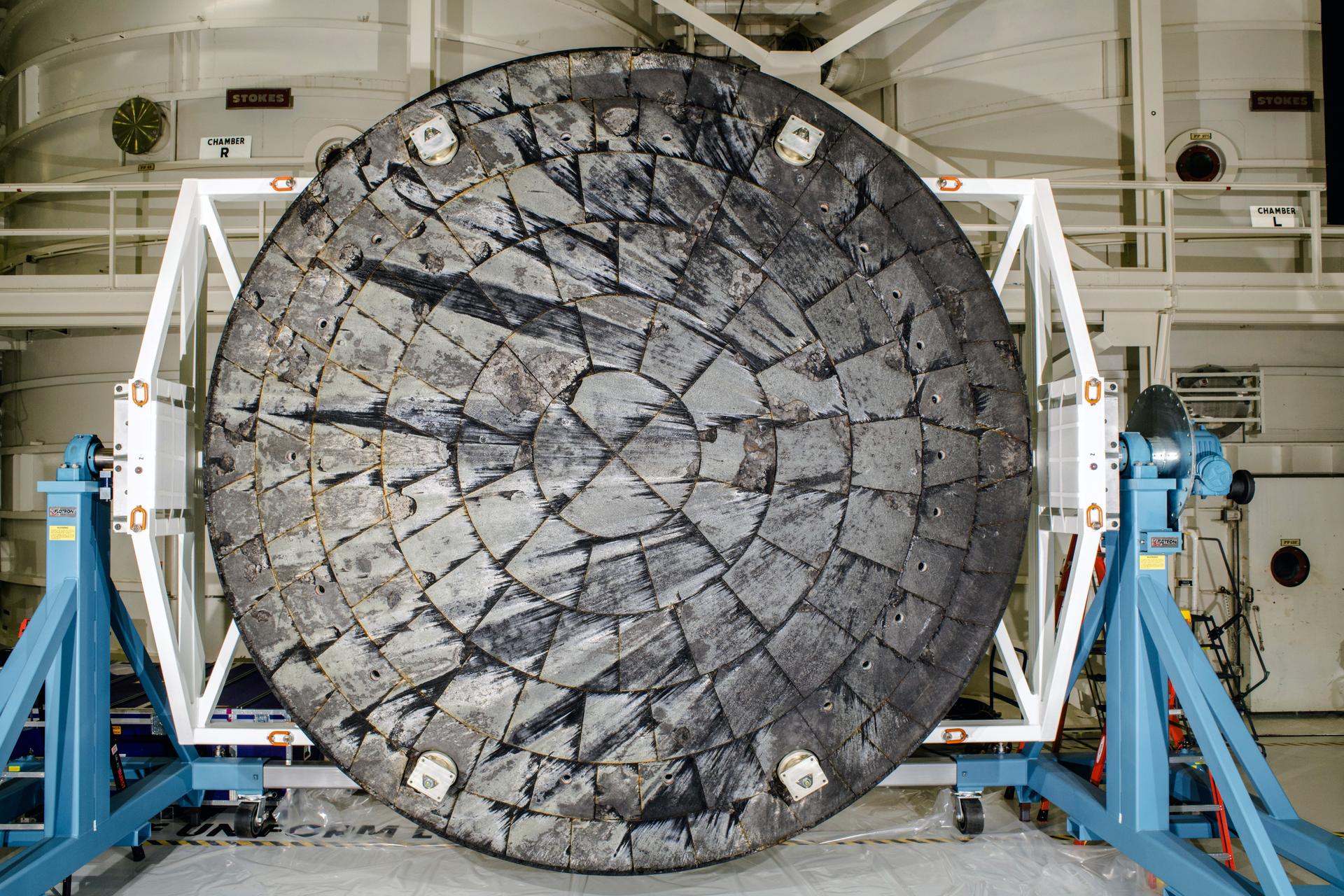
At the base of Orion, there are 186 blocks of a material called Avcoat, individually attached to provide a protective layer that allows the spacecraft to survive the heating of atmospheric reentry. Returning from the Moon, Orion encounters temperatures of up to 5,000° Fahrenheit (2,760° Celsius). A char layer that builds up on the outer skin of the Avcoat material is supposed to ablate, or erode, in a predictable manner during reentry. Instead, during Artemis I, fragments fell off the heat shield and left cavities in the Avcoat material.
Work by Saucedo and others—including substantial testing in ground facilities, wind tunnels, and high-temperature arc jet chambers—allowed engineers to find the cause of gases becoming trapped in the heat shield, leading to cracking. This was due to the Avcoat material being “impermeable,” essentially meaning it could not breathe.
After considering several options, including swapping the heat shield out for a newer one with more permeable Avcoat, NASA decided instead to change Orion’s reentry profile. For Artemis II, it would return through Earth’s atmosphere at a steeper angle, spending fewer minutes in the environment where this outgassing occurred during Artemis I. Much of Thursday’s meeting involved details about how the agency reached this conclusion and why the engineers deemed the approach safe.
A test block of Avcoat undergoes heat pulse testing inside an arc jet test chamber at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California. The test article, configured with both permeable (upper) and non-permeable (lower) Avcoat sections for comparison, helped to confirm an understanding of the root cause of the loss of charred Avcoat material on Artemis I.
Credit: NASA
A test block of Avcoat undergoes heat pulse testing inside an arc jet test chamber at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California. The test article, configured with both permeable (upper) and non-permeable (lower) Avcoat sections for comparison, helped to confirm an understanding of the root cause of the loss of charred Avcoat material on Artemis I. Credit: NASA
However, toward the end of the meeting, the NASA team agreed to discuss something that “no one really liked to talk about.” This was an analysis of what would happen to Orion if large sections of the heat shield failed completely during Artemis II. Formally, this is known as a “damage tolerance evaluation,” the engineers said. Informally, it’s known as “What if we’re wrong.”
The Avcoat blocks, which are about 1.5 inches thick, are laminated onto a thick composite base of the Orion spacecraft. Inside this is a titanium framework that carries the load of the vehicle. The NASA engineers wanted to understand what would happen if large chunks of the heat shield were stripped away entirely from the composite base of Orion. So they subjected this base material to high energies for periods of 10 seconds up to 10 minutes, which is longer than the period of heating Artemis II will experience during reentry.
What they found is that, in the event of such a failure, the structure of Orion would remain solid, the crew would be safe within, and the vehicle could still land in a water-tight manner in the Pacific Ocean.
“We have the data to say, on our worst day, we’re able to deal with that if we got to that point,” one of the NASA engineers said.
Getting to “flight rationale”
The composite layer beneath the heat shield is intended to withstand a maximum temperature of 500° F during reentry. During Artemis I, the maximum temperature recorded, despite the persistent cracking and char loss, was 160°. So any crew on board would have been safe. Even so, the heat shield damage was a serious concern because the agency’s modeling did not predict it.
After more than two years of testing and analysis of the char loss issue, the NASA engineers are convinced that, by increasing the angle of Orion’s descent during Artemis II, they can minimize damage to the heat shield. During Artemis I, as the vehicle descended from about 400,000 to 100,000 feet, it was under a “heat load” of various levels for 14 minutes. With Artemis II, this time will be reduced to eight minutes.
Orion’s entry profile will be similar for the first two and a half minutes, but afterward, the Artemis II entry will undertake a bit of a higher heat load than Artemis I for a couple of minutes. All of the agency’s modeling and extensive arc jet testing indicate this will produce significantly less cracking in the Avcoat material.
Much of the discussion Thursday delved into the technical minutiae of heat shields, tamp planes (the process of packing Avcoat into blocks), early char loss, spallation, and more. The discourse also revealed that one test in 2019, three years before Artemis I, indicated hints of the char loss later observed in flight. But this finding was not unequivocal, nor did it throw up a huge red flag at the time, the NASA officials said.
Technicians inspect the heat shield for the Artemis II launch. Credit: NASA
The message from Isaacman, Kshatriya, and other NASA officials at the meeting was clear. This heat shield was not perfect. If NASA knew several years ago what it knows now, the heat shield would be designed differently. It would be permeable to prevent the outgassing problems. Those changes are being incorporated into the Artemis III mission’s heat shield. There will be other tweaks to increase reliability.
Nevertheless, the agency is confident that flying the Artemis II heat shield on the revised profile is perfectly safe. In NASA jargon, such a rigorous justification that a space mission is safe to fly is known as flight rationale.
But why get to flight rationale at all? About 18 months ago, as the agency was narrowing in on the root cause of the heat shield issues, NASA’s leaders at the time, including Kshatriya, considered their options. They mulled the possibility of flying Artemis II in low-Earth orbit to test its life support equipment but not overly stress the heat shield. They thought about flying a second robotic mission around the Moon.
Perhaps most seriously, they considered moving forward with the Orion spacecraft (or at least its heat shield) that will be flown in Artemis III, which has permeable Avcoat, to be used for this mission. I asked Kshatriya on Thursday why they had not simply done this.
“We had considered ‘let’s just pull forward CSM 3 (the Artemis III spacecraft),’” he said, in part. “and essentially turn CSM 2 (Artemis II) either into a test article or something else. Again, CSM 3 has unique capabilities, docking systems on it, right? We didn’t have a docking mode for that mission (Artemis II). CSM 2 could not be retrofitted with the docking system because of the uniqueness of the tunnel. Really, CSM 2 is kind of uniquely a free return vehicle because of the way it was designed initially. So the mods that would have had to be made for (Artemis) II and III to do that swap would have been too odious, and we wouldn’t have gotten the learnings. And, you know, we’re trying to get up hill as quickly as we can.”
Given all of this, how should we feel about this flight rationale, with Artemis II potentially launching in early February?
Over the last 18 months, I have had many discussions with experts about this, from mid-level engineers and current and former astronauts to senior leaders. I know definitively that the four Artemis II astronauts, Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Jeremy Hansen, are comfortable with the decision. They did not feel that way at the beginning of the process. Wiseman, in particular, was quite skeptical. But they’ve been won over. Like almost everyone else who has reviewed NASA’s data at length, they accept the plan. Indeed, they are ready and eager to fly.
But what of the outside critics? That was the whole point of Thursday’s session. Could the NASA engineers convince Olivas and Camarda?
Yes, and maybe
Olivas flew two Space Shuttle missions in 2007 and 2009 and has an advanced degree in materials science from Rice University. Before this week’s meeting, he had not gone public with his heat shield concerns. But he has been talking to me and another space reporter, Robert Pearlman, for about a month now.
Olivas is very credible on these issues. He was asked by the NASA leadership in late 2023, before the independent review team was formally named, to provide a second set of eyes on the space agency’s heat shield work. He saw all of the investigative data in real time. Although not formally a member, he sat in on the review team’s meetings through 2024 before that process ended. Afterward, he had some lingering questions he felt were unresolved by that process. A few weeks ago, he told Pearlman and me he would be reluctant to fly on Orion. It was a stunning admission.
Isaacman appeared to take these concerns seriously. In advance of Thursday’s meeting, he engaged with Olivas to hear him out and share information about what NASA’s engineers had done over the last 18 months to resolve some of the independent review team’s questions. These included char loss very early in Orion’s reentry.
After Thursday’s meeting, Olivas told me he had changed his mind, expressing appreciation and admiration for the in-depth engineering work done by the NASA team. He would now fly on Orion.
Camarda, another former shuttle astronaut, was less effusive. He has been very public with his criticism of NASA’s handling of the Orion heat shield. He told me in December 2024 that the space agency and its leadership team should be “ashamed.” Unlike Olivas, however, he has been on the outside the whole time. NASA had kept Camarda, 73, at arm’s length, and he felt disrespected. Given his credentials—the aerospace engineer spent two decades working on thermal protection for the space shuttle and hypersonic vehicles–Camarda could be a potent voice of skepticism leading up to the Artemis II launch.
After the meeting, I asked Camarda whether he felt any better about flying crew on the Artemis II heat shield.
“I would never be happy accepting a workaround and flying something that I know is the worst version of that heat shield we could possibly fly and hoping that the workaround is going to fix it,” Camarda said. “What I really hope he [Isaacman] gets is that if we don’t get back to doing research at NASA, we’re not going to be able to help Starship solve their problems. We’ve got to get back to doing research.”
But Camarda was no longer the firebrand he was at the outset of the meeting. Near its end, in fact, he even thanked the leadership team for being brought in, read in on the data, and allowed to have his say.
Eric Berger is the senior space editor at Ars Technica, covering everything from astronomy to private space to NASA policy, and author of two books: Liftoff, about the rise of SpaceX; and Reentry, on the development of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon. A certified meteorologist, Eric lives in Houston.